Production-ready WiMax CPE design runs Linux
Nov 16, 2006 — by LinuxDevices Staff — from the LinuxDevices Archive — 9 views Freescale, Celestica, and Wavesat are jointly demonstrating a Linux-based reference design for WiMax CPE (customer premises equipment). The design features Freescale's PowerQUICC II Pro MPC8323E processor, Celestica's production-ready WiMax gateway “Solution Accelerator,” and Wavesat's Evolutive WiMax DM256… Mini-PCI module and MAC software.
Freescale, Celestica, and Wavesat are jointly demonstrating a Linux-based reference design for WiMax CPE (customer premises equipment). The design features Freescale's PowerQUICC II Pro MPC8323E processor, Celestica's production-ready WiMax gateway “Solution Accelerator,” and Wavesat's Evolutive WiMax DM256… Mini-PCI module and MAC software.
(Click for larger view of Celestica's CPE design)
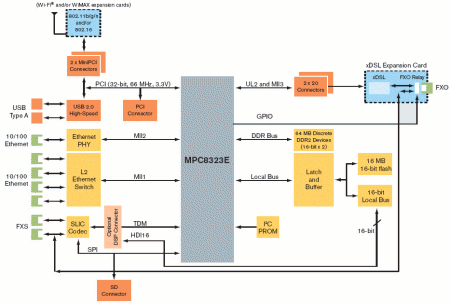
The companies are demonstrating the design at a Freescale Technology Forum event in Bangalore, India this week. The MPC8323E was designed by Freescale's India-based operation, which also designed the reference design depicted below, on which Celestica's design is partially based.
Freescale's MPC8323E-based WiMax CPE reference design diagram
(Click to enlarge)
The Celestica reference design is based on a Freescale-ported 2.6 Linux kernel. The design supports the WiMax Forum 802.16d-2004 certification (fixed WiMax), and is “designed for upgradeability” to 802.16e-2005 (mobile WiMax). Freescale cites In-Stat market research forecasting 16 million fixed and 15-25 million mobile WiMax subscribers by 2010.
Touted features include:
- Support for processor-and memory-intensive applications
- VOIP
- “advanced telephony”
- parental controls
- cryptographic operations
- Supports COTS (commercial, off-the-shelf) backhaul and LAN radios
- Cardbus ADSL/VDSL/VDSL2, HSDPA, and EVDO adapters
- Mini-PCI WiFi cards
The MPC8323E
The MPC8323E is based on an “e300c2” PowerPC core, clockable to 333MHz. The core was modified by removing the FPU (floating point unit) and adding a second integer unit. Together with a modified multiply instruction, this improves parallel processing efficiency for greater performance, Freescale says.
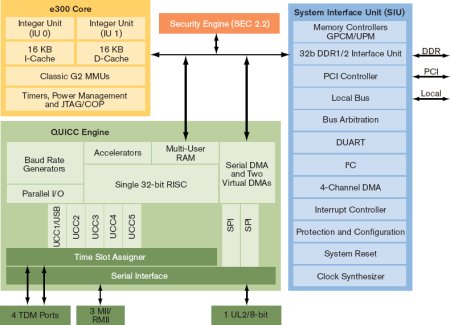
MPC8323E function block diagram
(Click to enlarge)
Additional touted features include:
- QUICC Engine block contains several peripheral controllers, and a 32-bit RISC controller that is microcode-programmable for NAT, Firewall, IPSec, and Advanced Quality of Service (QoS)
- 10/100 Mbps Ethernet
- HSE (hardware security engine) (in models with “E” suffix) processes DES, 3DES, AES, SHA-1, and MD-5
- Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) support up to OC-3 speeds
- Serial ATM
- Multi-physical layer (PHY) ATM
- High-level data link control (HDLC)
- Time division multiplexing (TDM)
- Binary synchronous communications protocol (BISYNC)
- UCC can also support USB 2.0 (full/low speed)
Lynelle McKay, GM of digital systems at Freescale, stated, “The addition of world class technology from Celestica [makes] the platform production-ready.”
Availability
Celestica's production-ready design appears to be available now. The MPC8323-series chip line comprises four models; availability was not disclosed.
Freescale also offers PowerQUICC III chips that target “long-term evolution” WiMax basestations.
This article was originally published on LinuxDevices.com and has been donated to the open source community by QuinStreet Inc. Please visit LinuxToday.com for up-to-date news and articles about Linux and open source.