Device profile: Smart Robots SR4 autonomous mobile robot
May 12, 2003 — by LinuxDevices Staff — from the LinuxDevices Archive — 15 viewsSmart Robots Inc. (Dalton, MA) demonstrated a new Linux-powered autonomous mobile robot platform at the 10th annual Trinity College Fire-Fighting Robot Contest held in Hartford, CT this past April. The SR4 can travel at a speed of approximately 1.5 ft/sec — which may not sound fast, but at that speed it can traverse a distance… equivalent to the length of three football fields in 10 minutes. It also can send and receive emails and host data pages on its built-in webserver.
 According to Smart Robots, the SR4 is designed to be physically and electronically expandable. The SR4's standard complement of sensors includes (depending on model) sonar, wheel encoders, a bumper belt, and an experimental position triangulation system based on ultrasonic beacon signals, controlled by its OOPic-R robot controller board. In addition, high-end SR4 models (“Professional” and up) also include an onboard Techsol Medallion HY7201 onboard computer running embedded Linux (and Java), and implement Internet connectivity including email and webserver functions.
According to Smart Robots, the SR4 is designed to be physically and electronically expandable. The SR4's standard complement of sensors includes (depending on model) sonar, wheel encoders, a bumper belt, and an experimental position triangulation system based on ultrasonic beacon signals, controlled by its OOPic-R robot controller board. In addition, high-end SR4 models (“Professional” and up) also include an onboard Techsol Medallion HY7201 onboard computer running embedded Linux (and Java), and implement Internet connectivity including email and webserver functions.
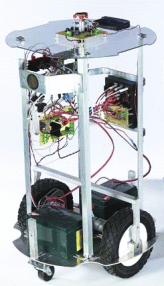 One especially interesting capability of the high-end SR4s is their capability to communicate over the Internet with other SR4s and with people — by email or via the built-in webserver. Basically, the robot creates and sends, or receives and interprets, XML-formatted emails; for example, the SR4 can diagnose its sensors and subsystems and automatically send trouble reports, and its internal webserver can provide real-time operating data for access anywhere on the Internet via web browser. Additionally, two or more wireless-enabled SR4s can communicate directly with each other (within range of their Wi-Fi signals) without any additional equipment.
One especially interesting capability of the high-end SR4s is their capability to communicate over the Internet with other SR4s and with people — by email or via the built-in webserver. Basically, the robot creates and sends, or receives and interprets, XML-formatted emails; for example, the SR4 can diagnose its sensors and subsystems and automatically send trouble reports, and its internal webserver can provide real-time operating data for access anywhere on the Internet via web browser. Additionally, two or more wireless-enabled SR4s can communicate directly with each other (within range of their Wi-Fi signals) without any additional equipment.
Here's a list of the SR4 robot's key features and specifications . . .
- Height — With body and dome; 3 ft. Without body and dome; 2 ft. 2 in.
- Diameter — with body, 18 in.; without body, 17 in.
- Speed — 1.5 ft. ft./sec. (three football fields in 10 minutes)
- Motor-wheel range — Minimum of three miles on a single battery charge
- Wheel size — 8 in. Diameter
- CPU — 60 MHz ARM processor
- Memory — SDRAM 32MB
- Data storage — 64MB Multimedia card
- Operating system — Linux; kernel version 2.4.19
- Programming languages — Java and C++ (with Visual Basic syntax supported as well on the OOPic robot controller board)
- Communications — Wireless 802.11b (Wi-Fi) to Web, PCs, LANs and other robots
- Connectivity — USB, Serial, I2C and Ethernet ports and connectors
- Robot control — OOPic robot controller board
- Batteries — Two 12v12Ah gel cell batteries; 1 electronics, 1 motors (provision for a third battery for addition of robot arm)
- Navigation — Map-based way-point navigation
- Sensors — Wheel encoders, beacon triangulation, bumpers, Polaroid sonar (obstacle avoidance), temperature
- Wheel encoder precision — Measures/detects approximately 0.157 in. incremental distance traveled
- Internet connectivity — onboard webserver for serving up data and overall web accessibility
- Motor-wheel configuration — two independent drive wheels (differential steering) and two casters (one spring loaded and the other offset from the ground — able to negotiate door jams and wheel chair ramps)
- Add-ons — Voice synthesis
Smart Robots said they expect to ship initial production units of the new SR4 autonomous robots in May, and that they plan to hold an international SR4 competition some time next next year.
This article was originally published on LinuxDevices.com and has been donated to the open source community by QuinStreet Inc. Please visit LinuxToday.com for up-to-date news and articles about Linux and open source.