Qualcomm chips can bump existing smartphones to dual cores
Dec 12, 2011 — by LinuxDevices Staff — from the LinuxDevices Archive — 6 viewsQualcomm announced new chips that will let smartphone manufacturers upgrade existing designs to dual cores with no other hardware or software changes. The MSM8625 and MSM8225 run at up to 1GHz, include integrated 3G modems, and will work as drop-in replacements for the existing MSM7x27A and MSM7x25A devices, the company says.
 We regularly whine that Qualcomm announces processors with few or no details, but the company seems to have become more self-effacing than ever. At the end of last week, the chipmaker made a quiet announcement of something quite significant: the ability for smartphone manufacturers to upgrade their existing devices to dual ARM cores by simply dropping in a new chip.
We regularly whine that Qualcomm announces processors with few or no details, but the company seems to have become more self-effacing than ever. At the end of last week, the chipmaker made a quiet announcement of something quite significant: the ability for smartphone manufacturers to upgrade their existing devices to dual ARM cores by simply dropping in a new chip.
According to Qualcomm, its new MSM8625 and MSM8225 chipsets are additions to its "Series 4" tier of Snapdragon processors. They feature dual-core CPUs operating at up to 1GHz, Adreno 203 GPUs (graphics processing units), and integrated 3G modems, the company says.
Qualcomm adds that the MSM8625 and MSM8225 are designed to be hardware- and software-compatible with the existing MSM7x27A and MSM7x25A chipsets ("mass market" devices that are in the company's System 1 tier). As a result, device manufacturers can "seamlessly replace their existing Snapdragon S1-based designs to S4 dual core-based designs."
Qualcomm noted that more than 100 million MSM7225 and MSM7227 chipsets have shipped. Smartphones based on these chipsets are operating on multiple carrier networks worldwide, the company added.
True to form, the chipmaker didn't release any further information. We presume that the MSM8625 and MSM8225 move from the 65nm fabrication of the chipsets they're designed to replace, to the 28nm of the other devices in the Series 4 tier.
Qualcomm did announce the "third generation" of its Qualcomm Reference Design (QRD) ecosystem program, designed to lower cost and development time for high-volume smartphones. The QRD program provides manufacturers with "pre-tested and optimized" hardware components (memory, sensors, touch panels, cameras, displays, RF, etc.) plus software applications and features (browsers, map/navigation, mail, music, instant messaging, fonts and languages, etc.), according to the company.
Other recent announcements
On Nov. 15, Qualcomm promoted eight new entries in the "System 4" tier of the company's Snapdragon line: the MSM8660A, MSM8260A, MSM8630, MSM8230, MSM8627, MSM8227, APQ8060A and APQ8030. Meanwhile, the company added, four members of its "System 1" tier have been upgraded: the MSM7225A, MSM7625A, MSM7227A, and MSM7627A.
(For background on the S1 through S4 tiers Qualcomm introduced in August in an attempt to "clarify" the Snapdragon range, see our earlier coverage.)
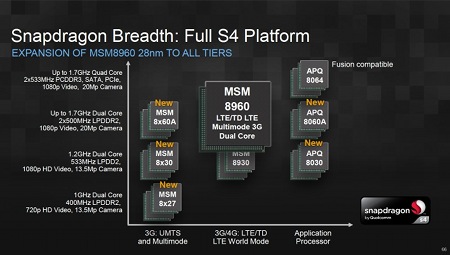
New additions to Qualcomm's Snapdragon S4 range
(Click to enlarge)
Somewhat more detail emerged via a slide (above) Qualcomm displayed at a Nov. 16 event it staged in New York for investors. According to this, the new S4 devices were to include:
- the MSM8x27, a 1GHz dual-core processor that supports 720p video and cameras up to 13.5 megapixels
- the MSM8x30, a 1.2GHz dual-core processor that supports 1080p video and cameras up to 13.5 megapixels
- the MSM8x60A, a 1.7GHz dual-core processor that supports 1080p video and cameras up to 20 megapixels
The slide reiterates that the top model in the S4 range — the APQ8064 that was first announced last February — will offer four cores and eight times the performance of the original Snapdragon. Meanwhile, the company noted in another slide (below), the "new" MSM8x60A represents a re-naming of the chip formerly known as the MSM8270 (first announced in 2009 as having a 1.2GHz "Scorpion" core and 45nm fabrication, then later switched to 28nm fabrication and a "Krait" core).
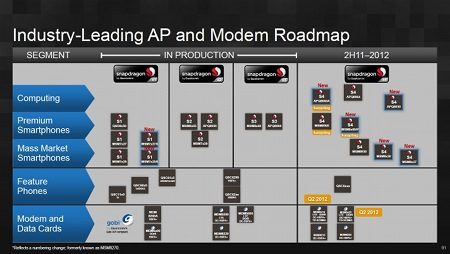
Qualcomm's latest processor roadmap
(Click to enlarge)
Further information
According to Qualcomm, the new MSM8625 and MSM8225 products will be available both as stand-alone chipsets and as part of the third-generation QRD platform in the first half of 2012.
General information on the company's Snapdragon chipsets may be found on the Snapdragon web page.
Jonathan Angel can be reached at [email protected] and followed at www.twitter.com/gadgetsense.
This article was originally published on LinuxDevices.com and has been donated to the open source community by QuinStreet Inc. Please visit LinuxToday.com for up-to-date news and articles about Linux and open source.