Linux robot car targets autonomous navigation
Jun 15, 2009 — by Eric Brown — from the LinuxDevices Archive — 21 views Tokyo-based ZMP Inc. is readying a Linux-based car robotics platform designed to test automotive robots and autonomous navigation algorithms. The RoboCar is built on a 500MHz AMD Geode LX800, and offers a stereo camera, multiple sensors, and an optional image recognition module, says the company.
Tokyo-based ZMP Inc. is readying a Linux-based car robotics platform designed to test automotive robots and autonomous navigation algorithms. The RoboCar is built on a 500MHz AMD Geode LX800, and offers a stereo camera, multiple sensors, and an optional image recognition module, says the company.
(Click for larger view of the RoboCar)
One-tenth the size of an actual automobile, the RoboCar is designed to enable development of vehicles with autonomous motion, accident-prevention safety technology, and intelligent transportation systems. It can also be used for testing of energy usage on electric or fuel-cell powered cars, and can be used as a general-purpose robotics platform for engineer training, says ZMP.
The RoboCar is touted as a more affordable and flexible platform for testing safety equipment and autonomous algorithms than using full-sized cars, and said to provide much more accurate maneuverability than the remote-control toys it resembles. Measuring 17 x 7.7 x 8.4 inches, and weighing a little over six pounds, the RoboCar starts at a price of $7,000, at least half the price of a full-sized test car, and requires correspondingly smaller, less expensive test facilities.
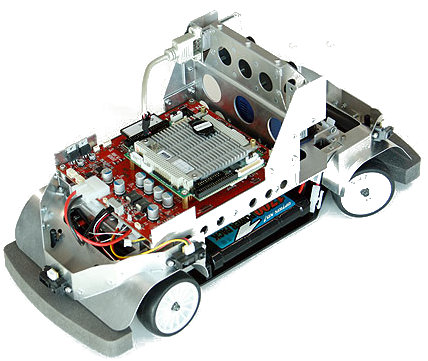
RoboCar without cover
The main Geode LX800 processor is run by a “soft real-time” version of embedded Linux, while the optional image recognition module, which runs off a NEC IMAPCAR parallel processor, is programmed by a dedicated real-time OS (RTOS). The company does not list memory options available with the RoboCar.

RoboCar with cover
The RoboCar uses 802.11 b/g/n WiFi for communications, and interacts with its environment using a stereo camera, which can be enhanced with the optional image recognition module. The robot also ships with gyro and acceleration sensors, infrared distance sensors, and independent rotary encoders for the four wheels and the main motor axis. A laser range finder is optional.


Detail views of RoboCar
(Click on either to enlarge)
The robot is powered by a 7.2V main NiMH battery pack, as well as a dozen 1.2V AA NiMH batteries for control systems. The RoboCar sports a carbon FRP chassis with double wishbone suspension, and an aluminum frame. The systems can be bought with or without a decorative covering, as pictured earlier in this story.
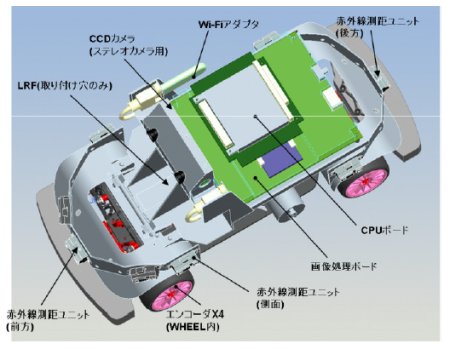
RoboCar diagram
(Click to enlarge)
The car is compatible with the MATLAB/Simulink control simulator software available on Linux and Windows desktops. A Linux API is said to be provided for development purposes. The WiFi module can be set up to communicate with multiple remote users as well as to communicate with other cars.
 RoboCar mainboard |
Specifications listed for the RoboCar include:
- Main processor — AMD Geode LX800 @ 500MHz
- Image processing module — optional, based on NEC IMAPCAR parallel processor
- WiFi — 802.11 b/g/n
- Camera — 2 x stereo VGA CCD camera (30fps)
- Sensors:
- 1 x gyroscope
- 3 x acceleration sensors
- 5 x rotary encoder (4 x for wheels; 1 x for main motor axis)
- 8 x infrared distance sensors
- 1 x laser range finder (optional)
- Power — DC power
- Battery — 1 x 7.2V NiMH battery pack; 12 x 1.2V AA NiMH batteries for control system
- Dimensions — 17.0 x 7.7 x 8.4 inches (429.0 x 195.0 x 212.2mm)
- Weight — 6.6 lbs (3K); carrying load 2.2 lbs (1K)
- Operating system — Linux (with soft real-time patch); image processing module controlled by “dedicated code”; GCC-based MATLAB/Simulink platform supports Linux and Windows desktop OSes
 Pino v2 |
ZMP stands for a walking algorithm called Zero Moment Point, and indeed, the company has built a number of humanoid robots, including the Linux-based Pino (pictured). Various version of the Pino have spawned a number of open source projects over the years. This Pino Project page hosted by Orion Technologies points to some other Pino groups, past and present.
The company plans to develop a larger, modified version of the RoboCar, with the goal of entering it into the Tsukuba Challenge robotics competition.
Availability
The RoboCar is available for order now, starting at $7,000 US without cover, with shipments schedule to begin by the end of the month. The company plans to manufacture 200 units in the first year. The image recognition module is available separately (in Japan only) for an additional JPY 399,000 (about $4,060), says ZMP. More information may be found here.
This article was originally published on LinuxDevices.com and has been donated to the open source community by QuinStreet Inc. Please visit LinuxToday.com for up-to-date news and articles about Linux and open source.