ATCA conference deems virtualization “best of show”
Oct 23, 2007 — by Eric Brown — from the LinuxDevices Archive — viewsVirtualLogix won its first “Best of Show” award at the recent AdvancedTCA Summit. Its Linux-based VLX for Network Infrastructure real-time virtualization software won in the “Best Software Product” category at last week's conference in Santa Clara, Calif., which showcased technology adhering to the Advanced Telecom Computing Architecture (AdvancedTCA).
AdvancedTCA (aka ATCA), encompasses a series of specifications that target the requirements of next-generation carrier grade telecommunications and networking equipment. The specifications, maintained by PICMG, define server blade and backplane form-factors with an eye toward maximized reliability, manageability, and serviceability. Applications for AdvancedTCA-compatible components and systems include telecom servers, gateways, wireless network controllers, and edge and access routers.
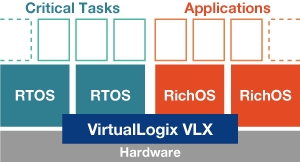
VLX system architecture
VirtualLogix's flagship VLX line of software combines a compact scheduler with various nanokernel components to share system resources between multiple heterogeneous operating system instances. The company claims that the technology helps reduce bill-of-material costs while encouraging legacy OS/application reuse, software failure containment, and license segregation.
 Typical AdvancedTCA processor blade |
VLX for Network Infrastructure specifically enables support of multiple operating systems onto a shared AdvancedTCA processor blade, enabling users to run Linux and RTOSes (real time operating systems) simultaneously. The company claims the solution helps achieve faster speeds and lower power consumption.
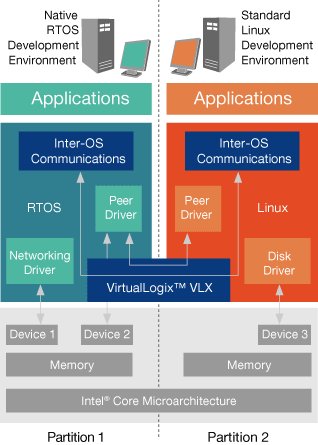
VLX for Network Infrastructure operating diagram
Mark Milligan, VirtualLogix VP of marketing, stated, “As the telecommunications industry rapidly adopts ATCA, developers increasingly look to real-time virtualization technology to improve performance while reducing costs, and power consumption in their next generation network equipment design.”
Competitors in the embedded virtualization space include Wind River, which in February acquired FSMLabs's real-time para-virtualization technology; Open Kernel Labs (OK Labs), whose real-time virtualizing microkernel is built into the Toshiba W47T mobile phone; and Sysgo, whose PikeOS includes para-virtualization technology that can host Linux as a guest OS. There is also some crossover competition from vendors of server-based virtualization software, such as VMware.
This article was originally published on LinuxDevices.com and has been donated to the open source community by QuinStreet Inc. Please visit LinuxToday.com for up-to-date news and articles about Linux and open source.